How Diet Impacts Acne, Psoriasis, and Other Skin Conditions
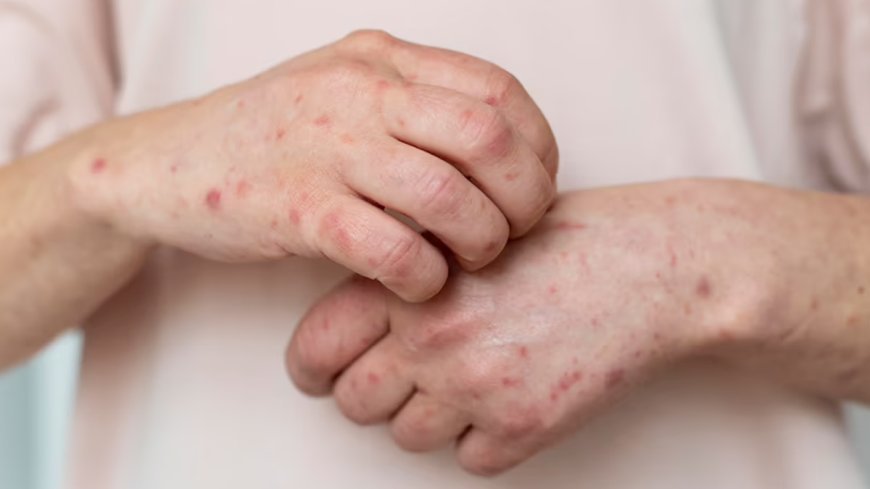
The relationship between food and skin health has become a growing concern, particularly for those suffering from skin diseases in Dubai(أمراض الجلد في دبي), where environmental stress and diet often interact. While many skin conditions like acne and psoriasis may appear to be purely genetic or environmental, evidence shows that diet plays a significant role in triggering or aggravating symptoms. Understanding how specific foods impact common skin diseases is essential for achieving clearer, healthier skin in both clinical and everyday settings.
The Gut-Skin Axis:
The connection between the gut and the skin, often referred to as the gut-skin axis, reveals how the digestive system influences skin health. Poor dietary choices can cause inflammation in the gut, which may lead to flare-ups of acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Processed foods, high sugar intake, and trans fats contribute to an unhealthy microbiome that can trigger inflammatory skin responses. On the other hand, fiber-rich foods and probiotics can restore gut balance and improve skin resilience.
Acne and Diet:
Acne is among the most common skin diseases and is closely linked to hormonal imbalances and excess oil production. Diets high in dairy products, refined carbs, and sugars can worsen acne by increasing insulin levels, which subsequently raises androgen levels and sebum production. People suffering from acne may benefit from reducing consumption of milk, white bread, and sweetened beverages. Meanwhile, omega-3 fatty acids from fish and flaxseed have shown anti-inflammatory effects, potentially reducing acne severity over time.
Psoriasis and Nutritional Triggers:
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by scaly, itchy plaques. While genetics are a key factor, diet can influence flare-ups. Foods high in saturated fats and alcohol may stimulate inflammatory pathways, worsening psoriasis symptoms. Gluten sensitivity has also been associated with some patients. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, leafy greens, and berries into the diet may help manage the severity of the condition. For residents managing skin diseases in Dubai, adapting to local foods that emphasize Mediterranean or plant-based diets can be especially beneficial.
Eczema and Food Sensitivities:
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, often flares up due to allergens, and food is a common culprit. In children and adults, eggs, peanuts, soy, and dairy are frequent triggers. Maintaining a food journal can help identify dietary triggers and prevent future outbreaks. Including foods rich in vitamins A, D, and E, such as sweet potatoes, salmon, and sunflower seeds, supports skin barrier function and reduces itching and redness. Staying hydrated in Dubai's hot climate is also essential for individuals prone to eczema and other skin diseases.
Rosacea and Dietary Management:
Rosacea affects the face with persistent redness and visible blood vessels, and certain foods can intensify these symptoms. Spicy foods, hot beverages, and alcohol are known to cause flare-ups. Individuals can manage rosacea more effectively by avoiding these triggers and opting for a cooling, anti-inflammatory diet. Cucumber, yogurt, and oatmeal are not only soothing when applied topically but also beneficial when consumed. Awareness of these effects can help individuals in Dubai minimize rosacea episodes without reliance solely on topical treatments.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa and the Role of Nutrition:
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a painful, chronic skin disease marked by deep nodules and abscesses, often in the underarm and groin areas. Studies suggest a strong link between diet and inflammation in HS. Foods with high glycemic indexes, dairy products, and processed meats can trigger symptoms. An elimination diet may assist in identifying food-related causes. Some patients have found relief by following anti-inflammatory, plant-based, or even ketogenic diets, which help regulate insulin and hormone levels.
The Role of Antioxidants and Micronutrients:
Vitamins and minerals play a vital role in preventing and managing skin diseases. Vitamin C aids collagen production and fights oxidative stress. Zinc contributes to immune function and is beneficial in managing acne and eczema. Selenium, found in nuts and fish, helps reduce inflammation in skin tissues. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise the skin barrier and immune defenses, making individuals more susceptible to infections and chronic conditions.
Hydration and Skin Function:
Hydration is often underestimated in discussions about skin health. In dry climates like Dubai, where transepidermal water loss is higher, insufficient water intake can lead to dryness, irritation, and worsening of existing skin diseases in Dubai. Drinking adequate water helps maintain skin elasticity and flushes out toxins. Foods with high water content—such as watermelon, cucumber, and citrus fruits—support hydration and promote a clearer complexion.
Food Allergies vs. Food Intolerances in Skin Reactions:
Not all adverse food reactions are allergies. Food intolerances may not show immediate symptoms but can cause delayed skin inflammation and chronic flare-ups. Dairy, gluten, and artificial additives often fall into this category. Identifying these through elimination diets or allergy testing can help clarify the root causes of skin issues. For individuals with skin diseases(أمراض الجلد), removing problematic foods often brings marked improvement in skin clarity and comfort.
Practical Diet Tips for Managing Skin Diseases:
To manage skin diseases effectively through diet, individuals should consider:
-
Keeping a consistent food diary to track skin reactions
-
Reducing consumption of high-glycemic and inflammatory foods
-
Increasing intake of antioxidants and omega-3-rich foods
-
Avoiding known allergens or intolerances
-
Staying hydrated with both water and water-rich foods
-
Consulting with a dermatologist and nutritionist for tailored plans
In Dubai, where cultural cuisine and climatic conditions vary, adapting dietary changes should take into account both nutritional value and lifestyle feasibility. Balanced dietary adjustments can serve as a cornerstone in managing skin diseases in Dubai effectively without complete reliance on medications or topical treatments.
Final Thoughts:
The impact of diet on skin health is more significant than most people realize. Whether it’s acne triggered by sugar, psoriasis worsened by processed fats, or eczema linked to food allergens, dietary choices can either inflame or improve skin conditions. For those managing skin diseases in Dubai, being aware of food triggers and nutrient-rich options is an empowering step toward healthier skin. With growing evidence supporting the gut-skin connection, it's clear that good health truly starts from within.
What's Your Reaction?

























































